# Load required packages
library(finalsize)
library(socialmixr)
library(MCMCpack)
library(readr)
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
# Load serological data
# source:
# Kwok KO, Cowling BJ, Wei VW, Wu KM, Read JM, Lessler J, Cummings DA, Peiris JS, Riley S.
# Social contacts and the locations in which they occur as risk factors for influenza infection.
# Proc Biol Sci. 2014 Aug 22;281(1789):20140709. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2014.0709.
# PMID: 25009062; PMCID: PMC4100506.
# https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/instance/4100506/
hk_serology <- readr::read_csv("https://github.com/epiverse-trace/howto/raw/refs/heads/main/data/rspb20140709supp2.csv")
# Allocate ages to bands
age_limits <- c(3,18,25,40,65)
age_group <- sapply(hk_serology$age,function(x){sum(x>=age_limits)})
hk_serology$age_group <- age_group
# Load HK social mixing data
contact_data <- socialmixr::contact_matrix(
polymod,
countries = "United Kingdom",
age.limits = age_limits,
symmetric = TRUE
)
demography_vector <- contact_data$demography$population
# Define model
model_function <- function(param){
r0 <- param[1]
alpha_val <- param[2]
contact_matrix = t(contact_data$matrix)
contact_matrix = contact_matrix / max(eigen(contact_matrix)$values)
names(demography_vector) = contact_data$demography$age.group
n_demo_grps = length(demography_vector)
contact_matrix = contact_matrix / demography_vector
susceptibility = matrix(
data = c(1, alpha_val*rep(1,n_demo_grps-1)),
n_demo_grps
)
n_risk_grps = 1L
p_susceptibility = matrix(1, n_demo_grps, n_risk_grps)
simulation_output <- finalsize::final_size(
r0 = r0,
contact_matrix = contact_matrix,
demography_vector = demography_vector,
susceptibility = susceptibility,
p_susceptibility = p_susceptibility,
solver = "iterative"
)
return(simulation_output)
}
# Define likelihood function
likelihood_function <- function(param,data) {
# Ensure positive parameters
if (any(param <= 0)) return(-Inf)
simulation_output <- model_function(param)
# Assuming non-informative priors for alpha and beta
log_prior <- 0 # Can refine if have different priors
# Calculate log-likelihood
test_positive <- hk_serology$ffold
log_likelihood <- log(
test_positive*simulation_output$p_infected[hk_serology$age_group] +
(1-test_positive)*(1-simulation_output$p_infected[hk_serology$age_group])
)
log_likelihood_total <- sum(log_likelihood)
# Check for valid output
if(is.na(log_likelihood_total)){
log_likelihood_total <- -Inf
}
# Return log-posterior (log-likelihood + log-prior)
return(log_likelihood_total + log_prior)
}
## Set up MCMCpack for Monte Carlo estimation
initial_param <- c(r0=1.5, alpha=0.8) # Initial guess for shape and rate
n_mcmc <- 1000
output <- MCMCpack::MCMCmetrop1R(
fun = likelihood_function,
theta.init = initial_param,
mcmc = n_mcmc, # Number of MCMC iterations
burnin = 100, # Burn-in period
verbose = FALSE, # Turn off verbose output
data = hk_serology
)
#>
#>
#> @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
#> The Metropolis acceptance rate was 0.55091
#> @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
# Plot outputs
data_summary <- stats::aggregate(
x = ffold ~ age_group,
data = hk_serology,
FUN = function(x){mean(x == 1)}
)
sample_outputs <- output[sample(1:n_mcmc,10),]
sample_simulate <- apply(sample_outputs,1,model_function)
# Combine all list elements into a single data frame
combined_data <- do.call(rbind, lapply(1:length(sample_simulate), function(i) {
cbind(sample_simulate[[i]], Simulation = i)
}))
combined_data$age_index <- base::match(
x = combined_data$demo_grp,
table = contact_data$demography$age.group
)
# Calculate mean and standard deviation of p_infected for each demo_grp
summary_data <- combined_data %>%
dplyr::group_by(age_index) %>%
dplyr::summarise(
Mean_p_infected = mean(p_infected),
SD_p_infected = sd(p_infected)
) %>%
dplyr::ungroup()
# Plotting
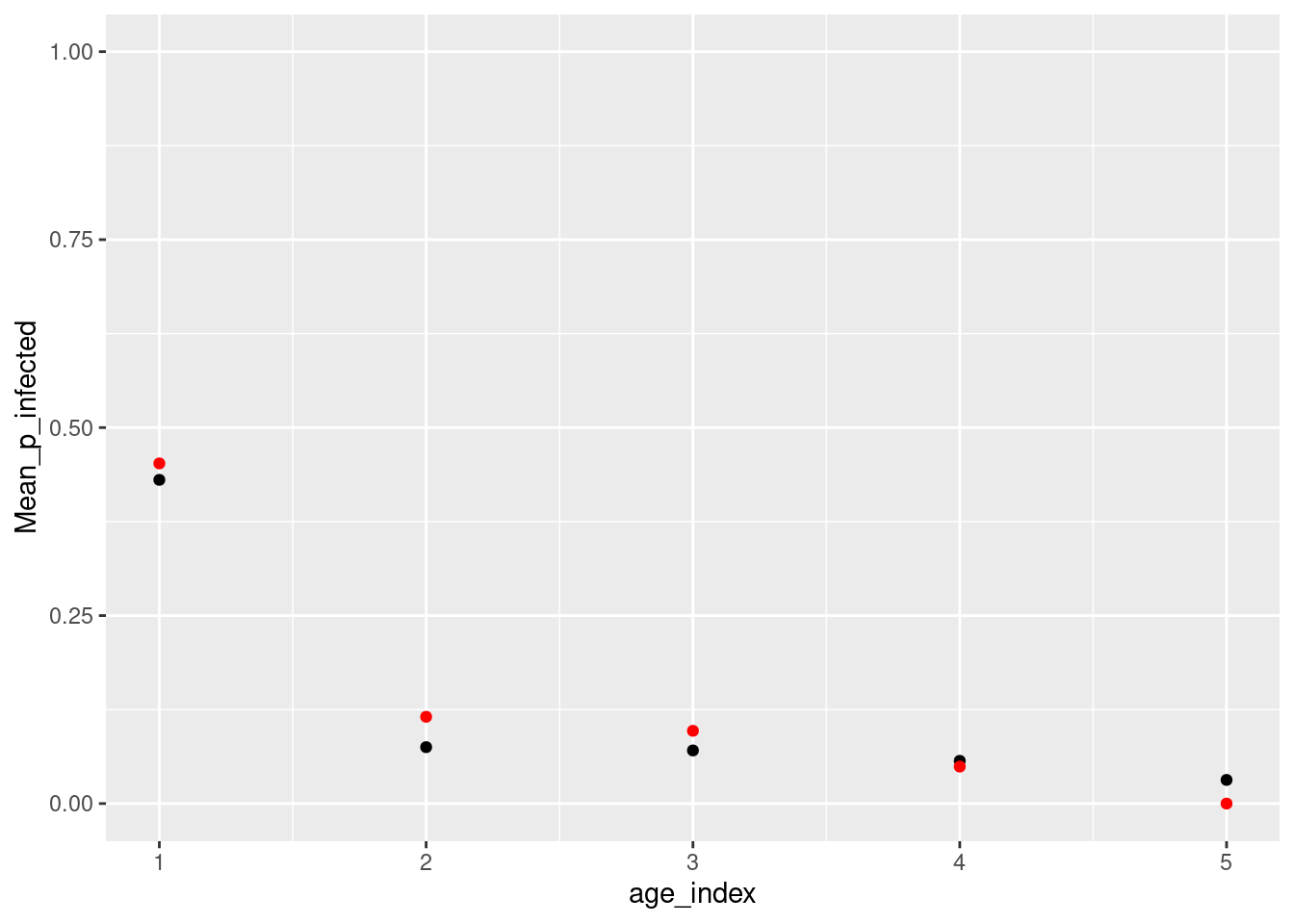
summary_data %>%
dplyr::left_join(data_summary, by = c("age_index" = "age_group")) %>%
ggplot() +
geom_point(aes(x = age_index, y = Mean_p_infected)) +
geom_point(aes(x = age_index, y = ffold),pch=19,col="red") +
ylim(0,1)