# Load packages
library(cleanepi)
library(linelist)
library(incidence2)
library(epiparameter)
library(EpiNow2)
library(tidyverse)
# Read data
dat <- subset(outbreaks::ebola_sim_clean$linelist ,!is.na(hospital)) %>%
dplyr::as_tibble()
# Print data
dat
#> # A tibble: 4,373 × 11
#> case_id generation date_of_infection date_of_onset date_of_hospitalisation
#> <chr> <int> <date> <date> <date>
#> 1 d1fafd 0 NA 2014-04-07 2014-04-17
#> 2 53371b 1 2014-04-09 2014-04-15 2014-04-20
#> 3 f5c3d8 1 2014-04-18 2014-04-21 2014-04-25
#> 4 0f58c4 2 2014-04-22 2014-04-26 2014-04-29
#> 5 f9149b 3 NA 2014-05-03 2014-05-04
#> 6 881bd4 3 2014-04-26 2014-05-01 2014-05-05
#> 7 e66fa4 2 NA 2014-04-21 2014-05-06
#> 8 20b688 3 NA 2014-05-05 2014-05-06
#> 9 40ae5f 4 2014-05-04 2014-05-07 2014-05-08
#> 10 f547d6 3 2014-05-02 2014-05-07 2014-05-08
#> # ℹ 4,363 more rows
#> # ℹ 6 more variables: date_of_outcome <date>, outcome <fct>, gender <fct>,
#> # hospital <fct>, lon <dbl>, lat <dbl>
# Get a linelist object
dat_linelist <- dat %>%
# create a linelist class object
linelist::make_linelist(
id = "case_id",
date_onset = "date_of_onset",
gender = "gender",
location = "hospital"
) %>%
# validate tagged variables
linelist::validate_linelist() %>%
# keep tagged and validated variables
linelist::tags_df()
# Print validated linelist
dat_linelist
#> # A tibble: 4,373 × 4
#> id date_onset gender location
#> <chr> <date> <fct> <fct>
#> 1 d1fafd 2014-04-07 f Military Hospital
#> 2 53371b 2014-04-15 m Connaught Hospital
#> 3 f5c3d8 2014-04-21 f other
#> 4 0f58c4 2014-04-26 f other
#> 5 f9149b 2014-05-03 f Connaught Hospital
#> 6 881bd4 2014-05-01 f Princess Christian Maternity Hospital (PCMH)
#> 7 e66fa4 2014-04-21 m other
#> 8 20b688 2014-05-05 m Rokupa Hospital
#> 9 40ae5f 2014-05-07 f Connaught Hospital
#> 10 f547d6 2014-05-07 f Connaught Hospital
#> # ℹ 4,363 more rows
# Get incidence object
dat_incidence <- dat_linelist %>%
# aggregate cases by date of onset by days
incidence2::incidence(
date_index = "date_onset",
interval = "day",
# rename column outputs for interoperability with {epinow2}
date_names_to = "date",
count_values_to = "confirm",
complete_dates = TRUE
) %>%
# keep date range between June and November 2014
dplyr::filter(date>="2014-06-01" & date<"2014-10-01") %>%
# drop column for interoperability with {epinow2}
dplyr::select(-count_variable)
# Print incidence data
dat_incidence
#> # A tibble: 122 × 2
#> date confirm
#> <date> <int>
#> 1 2014-06-01 0
#> 2 2014-06-02 3
#> 3 2014-06-03 1
#> 4 2014-06-04 0
#> 5 2014-06-05 1
#> 6 2014-06-06 3
#> 7 2014-06-07 4
#> 8 2014-06-08 1
#> 9 2014-06-09 4
#> 10 2014-06-10 1
#> # ℹ 112 more rows
# Generation time ---------------------------------------------------------
# Get serial interval delay
serial_interval <-
epiparameter::epiparameter_db(
disease = "ebola",
epi_name = "serial interval",
single_epiparameter = TRUE
)
# Print serial interval metadata
serial_interval
#> Disease: Ebola Virus Disease
#> Pathogen: Ebola Virus
#> Epi Parameter: serial interval
#> Study: WHO Ebola Response Team, Agua-Agum J, Ariyarajah A, Aylward B, Blake I,
#> Brennan R, Cori A, Donnelly C, Dorigatti I, Dye C, Eckmanns T, Ferguson
#> N, Formenty P, Fraser C, Garcia E, Garske T, Hinsley W, Holmes D,
#> Hugonnet S, Iyengar S, Jombart T, Krishnan R, Meijers S, Mills H,
#> Mohamed Y, Nedjati-Gilani G, Newton E, Nouvellet P, Pelletier L,
#> Perkins D, Riley S, Sagrado M, Schnitzler J, Schumacher D, Shah A, Van
#> Kerkhove M, Varsaneux O, Kannangarage N (2015). "West African Ebola
#> Epidemic after One Year — Slowing but Not Yet under Control." _The New
#> England Journal of Medicine_. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1414992
#> <https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc1414992>.
#> Distribution: gamma (days)
#> Parameters:
#> shape: 2.188
#> scale: 6.490
# Get distribution parameters from delay
serial_interval_param <- epiparameter::get_parameters(serial_interval)
# Adapt {epiparameter} to the {EpiNow2} distribution interface
serial_interval_gamma <- EpiNow2::Gamma(
shape = serial_interval_param["shape"],
scale = serial_interval_param["scale"]
)
# Print EpiNow2 output interface
serial_interval_gamma
#> - gamma distribution:
#> shape:
#> 2.2
#> rate:
#> 0.15
# Delays from infection to observed data ----------------------------------
# Get fixed delay from infection to symptom onset
incubation_period <- epiparameter::epiparameter_db(
disease = "ebola",
epi_name = "incubation",
single_epiparameter = TRUE
)
# Print incubation period metadata
incubation_period
#> Disease: Ebola Virus Disease
#> Pathogen: Ebola Virus
#> Epi Parameter: incubation period
#> Study: WHO Ebola Response Team, Agua-Agum J, Ariyarajah A, Aylward B, Blake I,
#> Brennan R, Cori A, Donnelly C, Dorigatti I, Dye C, Eckmanns T, Ferguson
#> N, Formenty P, Fraser C, Garcia E, Garske T, Hinsley W, Holmes D,
#> Hugonnet S, Iyengar S, Jombart T, Krishnan R, Meijers S, Mills H,
#> Mohamed Y, Nedjati-Gilani G, Newton E, Nouvellet P, Pelletier L,
#> Perkins D, Riley S, Sagrado M, Schnitzler J, Schumacher D, Shah A, Van
#> Kerkhove M, Varsaneux O, Kannangarage N (2015). "West African Ebola
#> Epidemic after One Year — Slowing but Not Yet under Control." _The New
#> England Journal of Medicine_. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1414992
#> <https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc1414992>.
#> Distribution: gamma (days)
#> Parameters:
#> shape: 1.578
#> scale: 6.528
# Get distribution parameters from delay
incubation_period_param <- epiparameter::get_parameters(incubation_period)
# Adapt {epiparameter} to the {EpiNow2} distribution interface
incubation_period_gamma <- EpiNow2::Gamma(
shape = incubation_period_param["shape"],
scale = incubation_period_param["scale"]
)
# Print EpiNow2 output interface
incubation_period_gamma
#> - gamma distribution:
#> shape:
#> 1.6
#> rate:
#> 0.15
# Estimate transmissibility -----------------------------------------------
# Configure parallel computation
withr::local_options(base::list(mc.cores = 4))
# WAIT this takes around 5 minutes
# tictoc::tic()
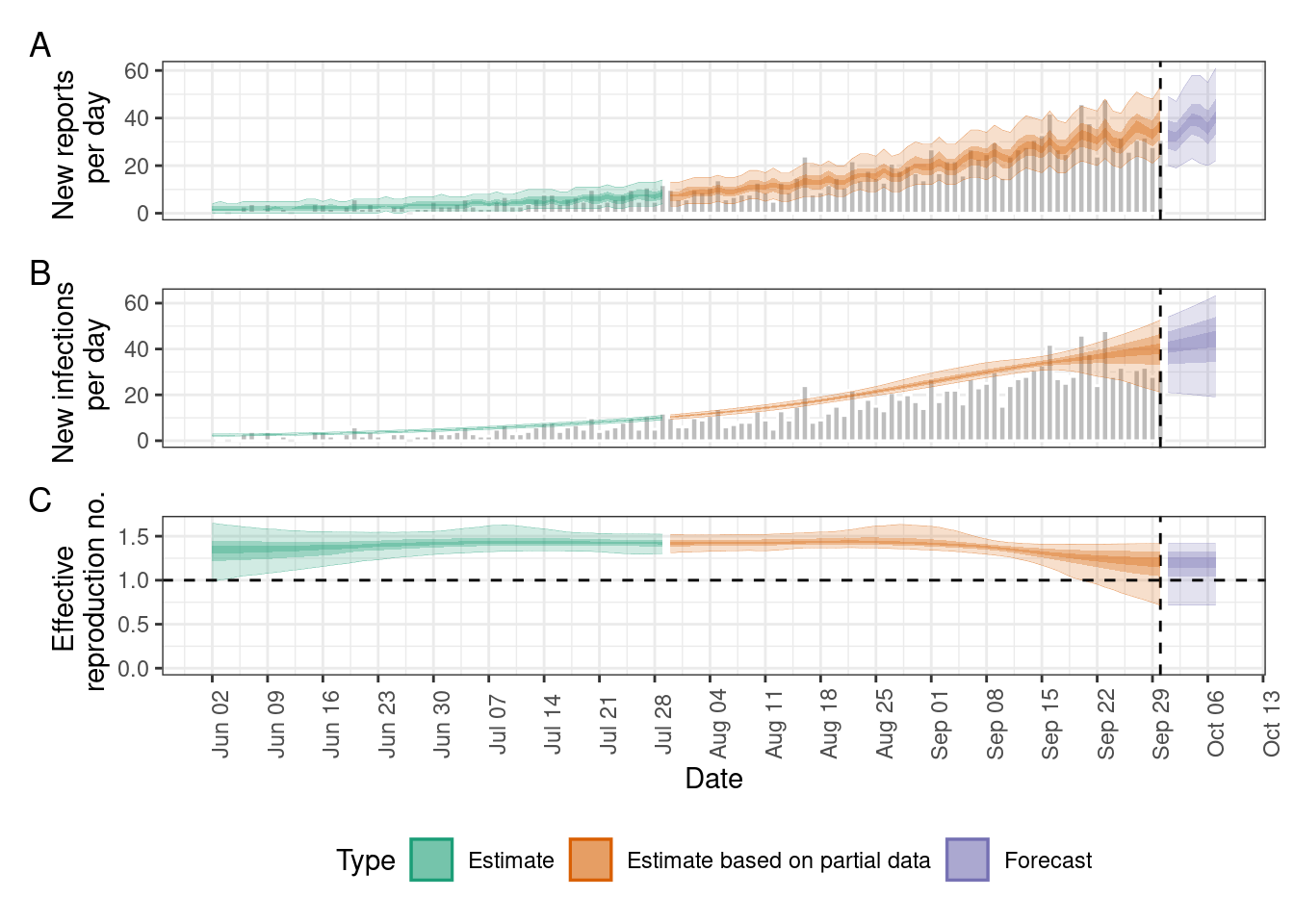
estimates <- EpiNow2::epinow(
data = dat_incidence,
generation_time = EpiNow2::generation_time_opts(serial_interval_gamma),
delays = EpiNow2::delay_opts(incubation_period_gamma)
)
#> WARN [2025-12-08 17:27:56] epinow: There were 88 divergent transitions after warmup. See
#> https://mc-stan.org/misc/warnings.html#divergent-transitions-after-warmup
#> to find out why this is a problem and how to eliminate them. -
#> WARN [2025-12-08 17:27:56] epinow: Examine the pairs() plot to diagnose sampling problems
#> -
#> WARN [2025-12-08 17:27:59] epinow: Bulk Effective Samples Size (ESS) is too low, indicating posterior means and medians may be unreliable.
#> Running the chains for more iterations may help. See
#> https://mc-stan.org/misc/warnings.html#bulk-ess -
#> WARN [2025-12-08 17:28:00] epinow: Tail Effective Samples Size (ESS) is too low, indicating posterior variances and tail quantiles may be unreliable.
#> Running the chains for more iterations may help. See
#> https://mc-stan.org/misc/warnings.html#tail-ess -
# tictoc::toc()
# Plot estimates
plot(estimates)