Summary and Schedule
This is an Epiverse-TRACE lesson built with The Carpentries Workbench.
| Setup Instructions | Download files required for the lesson | |
| Duration: 00h 00m | 1. Before we start |
Where can I meet other workshop participants? Where can I fill in my questions about the workshop topic? Where can I find the Code of Conduct? How can I report unacceptable behaviour? |
| Duration: 00h 10m | 2. Introduction |
Why to improve our code for analysis? What can we do to improve it? How can we start improving it? |
| Duration: 00h 20m | 3. Research compendium |
How do you create a research compendium for an R project? How do I facilitate users and collaborators to participate in my project? What features are related to sustainable software? |
| Duration: 00h 50m | 4. Reproducible analysis |
How do I make my research project reproducible? How do I include packages as dependencies of my project? What features are related to reproducible research? |
| Duration: 01h 50m | 5. README files |
Where can I give proper installation instructions? What licenses can I add for text, figures, and data? How do I generate a citation for my project? How can I increase the visibility of community guidelines? |
| Duration: 02h 35m | 6. Wrap up |
Where is a full view of the concepts covered today? How can I self-assess my progress using these tools? Where can I ask for questions after this workshop? Where can I write my feedback on this workshop? |
| Duration: 02h 47m | 7. Appendix |
Where can I add my functions? How do I need to document my functions? How can I read the documentation of my functions? How can I write a manuscript with my project outputs? |
| Duration: 02h 59m | 8. Definitions | How can I define Reliability, Usability and Sustainability? |
| Duration: 03h 09m | Finish |
The actual schedule may vary slightly depending on the topics and exercises chosen by the instructor.
Motivation
Have you ever wondered how cool would it be if you would be able to successfully:
- Reuse an analysis months or years later each time you need to revisit it?
- Redo the analyses, figures or tables after correcting an error in the data or following a reviewer’s recommendations?
- Reuse data from other authors for a secondary analysis thanks to informative metadata on the primary study?
Sadly, most of the time, this isn’t easy because:
- We do not remember how we did the analysis,
- Redoing figures and tables is time-consuming,
- Data is not readily available or unreadable today.
In this lesson, you will learn how to improve your code’s reliability, usability and sustainability for epidemic analysis with R packages. You will learn how to add specific features to your R project to keep it as Open, Reproducible, and Sustainable as possible!

Prerequisite
In this lesson, we will use R, Git, and GitHub. Some previous experience using RStudio projects is expected, but isn’t mandatory.
For an introductory lesson on Git, please go to the Version Control with Git in Rstudio lesson.
Software Setup
Install Rstudio
Install R and Rstudio https://posit.co/download/rstudio-desktop/
Create a GitHub account
Create a GitHub account https://github.com/
Install Git
Follow software specific suggestions
Follow happygitwithr recommendation for each Operating system.
For Windows
For MacOS
For Linux
Install R packages
These installation steps could ask you
? Do you want to continue (Y/n) write y and
press ENTER. It can take up to 3 minutes to complete.
First, we strongly suggest installing the development versions of the
rcompendium and {rrtools} packages, and
others like usethis and renv, using the
following code chunk:
R
if(!require("pak")) install.packages("pak")
new <- c("FRBCesab/rcompendium",
"benmarwick/rrtools",
"usethis",
"tidyverse",
"here",
"yaml",
"renv")
pak::pak(new)
Configure Git and GitHub
Follow all these steps
In these steps, we will verify that you have:
- a correctly configured token, and
- a clean output when running
usethis::git_sitrep().
1. Verify your git configuration
Use gh::gh_whoami() to check if your local git
configuration recognizes:
- your name
- your GitHub account
- your token
R
gh::gh_whoami()
OUTPUT
{
"name": "Andree Valle Campos",
"login": "avallecam",
"html_url": "https://github.com/avallecam",
"scopes": "gist, repo, workflow",
"token": "gho_...AlAn"
}
If there is no name, login, or
html_url, then you need to run:
R
gert::git_config_global_set(name = "user.name", value = "John Doe")
gert::git_config_global_set(name = "user.email", value = "john.doe@domain.com")
gert::git_config_global_set(name = "github.user", value = "jdoe")
If you do not have a token, follow step number 3.
2. Get a situational report on your current Git/GitHub status:
Use usethis::git_sitrep() to check if there is no
✖ ... line in the output with an error message.
An example with two errors is below:
R
usethis::git_sitrep()
ERROR
✖ Token lacks recommended scopes:
- 'user:email': needed to read user's email addresses
Consider re-creating your PAT with the missing scopes.
`create_github_token()` defaults to the recommended scopes.
✖ Can't retrieve registered email addresses from GitHub.
Consider re-creating your PAT with the 'user' or at least 'user:email' scope.The output shows that I had a token but must fix its configuration. If you do not have a token or get a similar error message, follow the next step.
If you have an error message unrelated to creating a token, copy and paste this output in your issue report to the email at the end of this page.
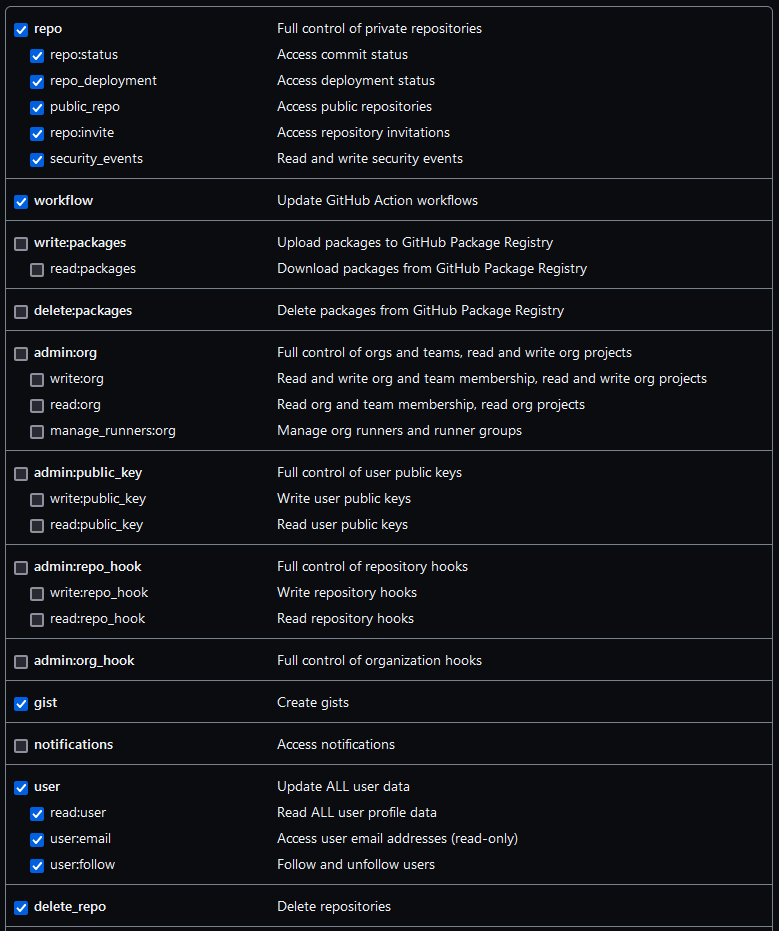
3. Create your GitHub token:
Do this with usethis::create_github_token(). This
function should redirect you to GitHub on your browser. Once there,
check all the options in the figure below.
R
usethis::create_github_token()
Check all of the following options:
4. Configure your token
To complete the configuration of your token use
gitcreds::gitcreds_set() (Bryan, 2023), then
accept that you want to 2: Replace these credentials. Do
this by writing the number 2 and press ENTER.
R
gitcreds::gitcreds_set()
OUTPUT
-> What would you like to do?
1: Abort update with error, and keep the existing credentials
2: Replace these credentials
3: See the password / token
Selection: 2
Paste your token to save it and complete this step.
5. Run again the situational report:
Verify again that there is no ✖ ... line in the output
with an error message. The expected outcome should look like this:
R
usethis::git_sitrep()
OUTPUT
Git config (global)
• Name: 'Andree Valle'
• Email: 'avallecam@gmail.com'
• Global (user-level) gitignore file: <unset>
• Vaccinated: FALSE
ℹ See `?git_vaccinate` to learn more
• Default Git protocol: 'https'
• Default initial branch name: 'master'
GitHub
• Default GitHub host: 'https://github.com'
• Personal access token for 'https://github.com': '<discovered>'
• GitHub user: 'avallecam'
• Token scopes: 'delete_repo, gist, repo, user, workflow'
• Email(s): 'avallecam@gmail.com (primary)', 'andree.valle-campos@lshtm.ac.uk'
Git repo for current project
ℹ No active usethis projectIf you still have an error, close Rstudio and open it again for changes to take effect.
If the error persist, copy and paste this output in your issue report to the email at the end of this page.
6. Two-factor authentication
If you have an error message related to Two-factor authentication, follow the steps in this GitHub guide.
Configure your R environment
Follow all these steps
1. Set the default Git branch name
Run the code chunk below:
R
usethis::git_default_branch_configure(name = "main")
This step will homogenize the name of the default branch in our computers. We need this to make some auto-generated links work downstream.
2. Add {rcompendium} credentials
Use rcompendium::set_credentials() to paste your name
and personal information to the .Rprofile configuration
file.
Adapt the code chunk below to your name, family name, email, and ORCID. Adding your ORCID is optional.
R
rcompendium::set_credentials(
given = "Andree",
family = "Valle-Campos",
email = "avallecam@gmail.com",
orcid = "0000-0002-7779-481X"
)
This function will automatically copy a line of code to the clipboard
that starts with options(..., and open a file called
.Rprofile. Paste the line of code in the file. After this,
close Rstudio and open it again for changes to take effect.
You can access the content of the .Rprofile file at any
time with usethis::edit_r_profile().
Your Questions
If you need any assistance installing the software, configuring Git and GitHub, or have any other questions about the workshop, please send an email to andree.valle-campos@lshtm.ac.uk
