Summary and Schedule
This is an Epiverse-TRACE tutorial built with The Carpentries Workbench.
| Setup Instructions | Download files required for the lesson | |
| Duration: 00h 00m | 1. Read case data |
Where do you usually store outbreak data? What data formats do you commonly use for analysis? Can you import data directly from servers and health information systems? :::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::: |
| Duration: 00h 30m | 2. Clean case data |
How to clean and standardize case
data? :::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::: |
| Duration: 01h 10m | 3. Validate case data |
How to convert a raw dataset into a linelist object?
|
| Duration: 01h 22m | 4. Aggregate and visualize |
How to aggregate and summarise case data? How to visualize aggregated data? What is distribution of cases across time, space, gender, and age? |
| Duration: 01h 52m | Finish |
The actual schedule may vary slightly depending on the topics and exercises chosen by the instructor.
Motivation
Outbreaks of infectious diseases can appear as a result of different pathogens, and in different contexts, but they typically lead to similar public health questions, from understanding patterns of transmission and severity to examining the effect of control measures (Cori et al. 2017). We can relate each of these public health questions to a series of outbreak data analysis tasks. The more efficiently and reliably we can perform these tasks, the faster and more accurately we can answer the underlying questions.
Epiverse-TRACE aims to provide a software ecosystem for outbreak analytics with integrated, generalisable and scalable community-driven software. We support the development of new R packages, help link together existing tools to make them more user-friendly, and contribute to a community of practice, spanning field epidemiologists, data scientists, lab researchers, health agency analysts, software engineers and more.
Epiverse-TRACE tutorials
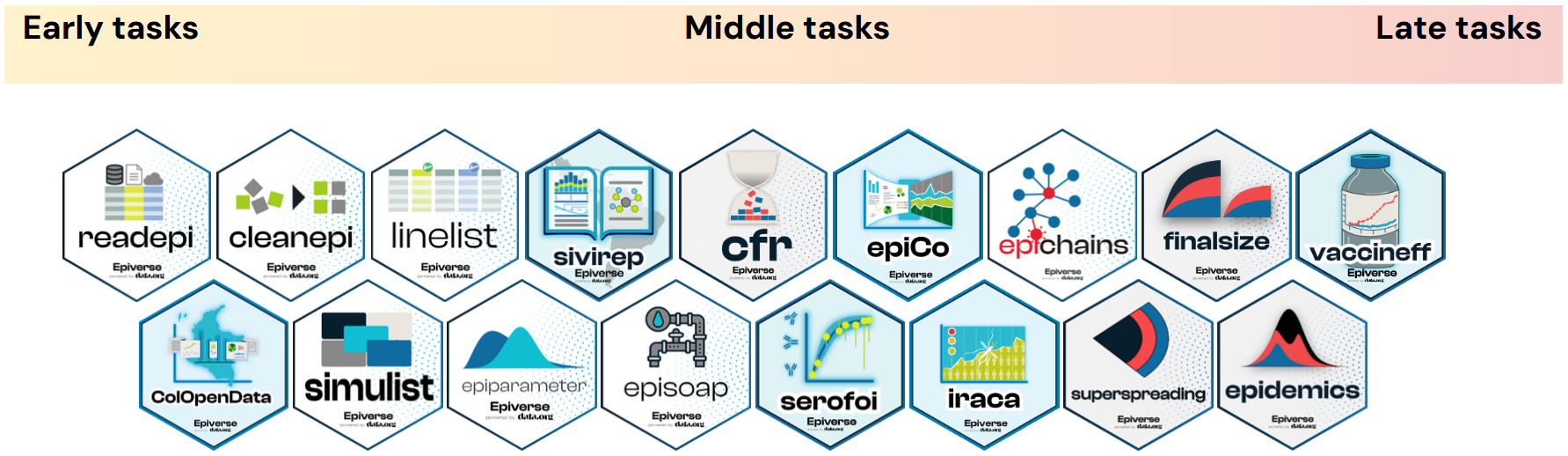
Our tutorials are built around an outbreak analysis pipeline split into three stages: Early tasks, Middle tasks and Late tasks. The outputs of tasks completed in earlier stages commonly feed into the tasks required for later ones.
Each task has its tutorial website and each tutorial website consists of a set of episodes covering different topics.
| Early task tutorials ➠ | Middle task tutorials ➠ | Late task tutorials ➠ |
|---|---|---|
| Read and clean case data, and make linelist | Real-time analysis and forecasting | Scenario modelling |
| Read, clean and validate case data, convert linelist data to incidence for visualization. | Access delay distributions and estimate transmission metrics, forecast cases, estimate severity and superspreading. | Simulate disease spread and investigate interventions. |
Each episode contains:
- Overview: describes what questions will be answered and the objectives of the episode.
- Prerequisites: describes what episodes/packages ideally need to be covered before the current episode.
- Example R code: example R code so you can work through the episodes on your own computer.
- Challenges: challenges that can be completed to test your understanding.
- Explainers: boxes to enhance your understanding of mathematical and modelling concepts.
Also check out the glossary for any terms you may be unfamiliar with.
Epiverse-TRACE R packages
Our strategy is to gradually incorporate specialised R packages into a traditional analysis pipeline. These packages should fill the gaps in these epidemiology-specific tasks in response to outbreaks.
Prerequisite
This content assumes intermediate R knowledge. This tutorials are for you if:
- You can read data into R, transform and reshape data, and make a wide variety of graphs
- You are familiar with functions from dplyr, tidyr, and ggplot2
- You can use the magrittr pipe
%>%and/or native pipe|>.
We expect learners to have some exposure to basic Statistical, Mathematical and Epidemic theory concepts, but NOT intermediate or expert familiarity with modeling.
Software Setup
Follow these two steps:
1. Install or upgrade R and RStudio
R and RStudio are two separate pieces of software:
- R is a programming language and software used to run code written in R.
- RStudio is an integrated development environment (IDE) that makes using R easier. We recommend to use RStudio to interact with R.
To install R and RStudio, follow these instructions https://posit.co/download/rstudio-desktop/.
Already installed?
Hold on: This is a great time to make sure your R installation is current.
This tutorial requires R version 4.0.0 or later.
To check if your R version is up to date:
In RStudio your R version will be printed in the console window. Or run
sessionInfo().-
To update R, download and install the latest version from the R project website for your operating system.
After installing a new version, you will have to reinstall all your packages with the new version.
For Windows, the installr package can upgrade your R version and migrate your package library.
To update RStudio, open RStudio and click on
Help > Check for Updates. If a new version is available follow the instructions on the screen.
Check for Updates regularly
While this may sound scary, it is far more common to run into issues due to using out-of-date versions of R or R packages. Keeping up with the latest versions of R, RStudio, and any packages you regularly use is a good practice.
2. Check and Install Build Tools
Some packages require a complementary set of tools to build them. Open RStudio and copy and paste the following code chunk into the console window, then press the Enter (Windows and Linux) or Return (MacOS) to execute the command:
R
if(!require("pkgbuild")) install.packages("pkgbuild")
pkgbuild::check_build_tools(debug = TRUE)
We expect a message like the one below:
OUTPUT
Your system is ready to build packages!If the build tools are not available, this will trigger an automated install.
- Run the command in the console.
- Don’t interrupt it—wait until R prints the confirmation message.
- Once that’s done, restart your R session (or just restart RStudio) to ensure the changes take effect.
If the automatic installation does not work, you can manually install them according to your operating system.
Environment Check
This step requires administrator privileges to install software.
If you do not have admin rights in your current environment:
- Try running the tutorial on your personal machine
where you have full access.
- Use a preconfigured development environment
(e.g. Posit Cloud).
- Ask your system administrator to install the required software for you.
3. Install the required R packages
Open RStudio and copy and paste the following code chunk into the console window, then press the Enter (Windows and Linux) or Return (MacOS) to execute the command:
R
# for episodes on read, clean, validate and visualize linelist
if(!require("pak")) install.packages("pak")
new_packages <- c(
"epiverse-trace/readepi@readepi_no_his_spc_deps",
"cleanepi@1.1.0",
"reactable",
"rio",
"here",
"DBI",
"RSQLite",
"dbplyr",
"linelist",
"simulist",
"incidence2",
"epiverse-trace/tracetheme",
"tidyverse"
)
pak::pkg_install(new_packages)
These installation steps could ask you
? Do you want to continue (Y/n) write Y and
press Enter.
If you get an error message when installing
{tracetheme}, try this alternative code:
R
# for tracetheme
install.packages("tracetheme", repos = c("https://epiverse-trace.r-universe.dev"))
Try using the classical code function to install one package, for example:
R
install.packages("rio")
If the error message keyword include an string like
Personal access token (PAT), you may need to set
up your GitHub token.
First, install these R packages:
R
if(!require("pak")) install.packages("pak")
new <- c("gh",
"gitcreds",
"usethis")
pak::pak(new)
Then, follow these three steps to set up your GitHub token (read this step-by-step guide):
R
# Generate a token
usethis::create_github_token()
# Configure your token
gitcreds::gitcreds_set()
# Get a situational report
usethis::git_sitrep()
Try again installing {tracetheme}:
R
if(!require("remotes")) install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("epiverse-trace/tracetheme")
If the error persist, contact us!
You should update all of the packages required for the tutorial, even if you installed them relatively recently. New versions bring improvements and important bug fixes.
When the installation has finished, you can try to load the packages by pasting the following code into the console:
R
# for episodes on read, clean, validate and visualize linelist
library(readepi)
library(cleanepi)
library(reactable)
library(rio)
library(here)
library(DBI)
library(RSQLite)
library(dbplyr)
library(linelist)
library(simulist)
library(incidence2)
library(tracetheme)
library(tidyverse)
If you do NOT see an error like
there is no package called ‘...’ you are good to go! If you
do, contact us!
4. Setup an RStudio project and folder
We suggest to use RStudio Projects.
Follow these steps
- Create an RStudio Project. If needed, follow this how-to guide on “Hello RStudio Projects” to create a New Project in a New Directory.
-
Create the
data/folder inside the RStudio project or corresponding directory. Use thedata/folder to save the data sets to download.
The directory of an RStudio Project named, for example
training, should look like this:
training/
|__ data/
|__ training.RprojRStudio Projects allows you to use relative
file paths with respect to the R Project, making your
code more portable and less error-prone. Avoids using
setwd() with absolute paths like
"C:/Users/MyName/WeirdPath/training/data/file.csv".
5. Create a GitHub Account
We can use GitHub as a collaboration platform to communicate package issues and engage in community discussions.
Follow all these steps
- Go to https://github.com and follow the “Sign up” link at the top-right of the window.
- Follow the instructions to create an account.
- Verify your email address with GitHub.
Data sets
Download the data
We will download the data directly from R during the tutorial. However, if you are expecting problems with the network, it may be better to download the data beforehand and store it on your machine.
The data files for the tutorial can be downloaded manually here:
- https://epiverse-trace.github.io/tutorials-early/data/ebola_cases_2.csv
- https://epiverse-trace.github.io/tutorials-early/data/Marburg.zip
- https://epiverse-trace.github.io/tutorials-early/data/simulated_ebola_2.csv
- https://epiverse-trace.github.io/tutorials-early/data/delta_full-messy.csv
- https://epiverse-trace.github.io/tutorials-early/data/linelist-date_of_birth.csv
Your Questions
If you need any assistance installing the software or have any other questions about this tutorial, please send an email to andree.valle-campos@lshtm.ac.uk
