Getting started with modelling interventions targeting social contacts
Source:vignettes/modelling_interventions.Rmd
modelling_interventions.RmdCode
Prepare population and initial conditions
Prepare population and contact data.
Note on social contacts data
epidemics expects social contacts matrices \(M_{ij}\) to represent contacts to \(i\) from \(j\) (Wallinga, Teunis, and Kretzschmar 2006), such that \(q M_{ij} / n_i\) is the probability of infection, where \(q\) is a scaling factor dependent on infection transmissibility, and \(n_i\) is the population proportion of group \(i\).
Social contacts matrices provided by the socialmixr package follow the opposite convention, where \(M_{ij}\) represents contacts from group \(i\) to group \(j\).
Thus social contact matrices from socialmixr need to be transposed (using t()) before they are used with epidemics.
Code
# load contact and population data from socialmixr::polymod
polymod <- socialmixr::polymod
contact_data <- socialmixr::contact_matrix(
polymod,
countries = "United Kingdom",
age.limits = c(0, 20, 40),
symmetric = TRUE
)
#> Removing participants that have contacts without age information. To change this behaviour, set the 'missing.contact.age' optionCode
Prepare initial conditions for each age group.
Code
# initial conditions
initial_i <- 1e-6
initial_conditions <- c(
S = 1 - initial_i, E = 0, I = initial_i, R = 0, V = 0
)
# build for all age groups
initial_conditions <- rbind(
initial_conditions,
initial_conditions,
initial_conditions
)
# assign rownames for clarity
rownames(initial_conditions) <- rownames(contact_matrix)Prepare a population as a population class object.
Code
uk_population <- population(
name = "UK",
contact_matrix = contact_matrix,
demography_vector = demography_vector,
initial_conditions = initial_conditions
)Prepare an intervention
Prepare an intervention to simulate school closures.
Code
# prepare an intervention with a differential effect on age groups
close_schools <- intervention(
name = "School closure",
type = "contacts",
time_begin = 200,
time_end = 300,
reduction = matrix(c(0.5, 0.001, 0.001))
)
# examine the intervention object
close_schools
#> <contacts_intervention> object
#>
#> Intervention name:
#> "School closure"
#>
#> Begins at:
#> [1] 200
#>
#> Ends at:
#> [1] 300
#>
#> Reduction:
#> Interv. 1
#> Demo. grp. 1 0.500
#> Demo. grp. 2 0.001
#> Demo. grp. 3 0.001Run epidemic model
Code
# run an epidemic model using `epidemic`
output <- model_default(
population = uk_population,
intervention = list(contacts = close_schools),
time_end = 600, increment = 1.0
)Prepare data and visualise infections
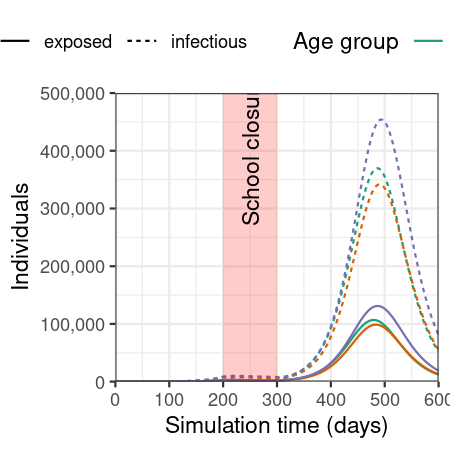
Plot epidemic over time, showing only the number of individuals in the exposed and infected compartments.
Code
# plot figure of epidemic curve
filter(output, compartment %in% c("exposed", "infectious")) %>%
ggplot(
aes(
x = time,
y = value,
col = demography_group,
linetype = compartment
)
) +
geom_line() +
annotate(
geom = "rect",
xmin = close_schools$time_begin,
xmax = close_schools$time_end,
ymin = 0, ymax = 500e3,
fill = alpha("red", alpha = 0.2),
lty = "dashed"
) +
annotate(
geom = "text",
x = mean(c(close_schools$time_begin, close_schools$time_end)),
y = 400e3,
angle = 90,
label = "School closure"
) +
scale_y_continuous(
labels = scales::comma
) +
scale_colour_brewer(
palette = "Dark2",
name = "Age group"
) +
expand_limits(
y = c(0, 500e3)
) +
coord_cartesian(
expand = FALSE
) +
theme_bw() +
theme(
legend.position = "top"
) +
labs(
x = "Simulation time (days)",
linetype = "Compartment",
y = "Individuals"
)